Introduction:-
In today’s fast-paced digital world, where mobile apps and websites play a crucial role in connecting businesses with their customers, the importance of thorough testing cannot be overstated. As consumers’ expectations for seamless and high-quality user experiences continue to rise, developers and quality assurance teams are faced with the daunting task of ensuring their applications work flawlessly on a wide array of devices and in real-world scenarios. This is where Real Device Testing (RDT) steps in as a pivotal component of the testing process. In this blog, we’ll dive into the world of RDT, exploring its significance, capabilities, and why it has become indispensable for mobile app and web testing.“Putting Apps to the Real-World Test: Unveiling Real Device Testing”
Before delving into its capabilities and its future, let’s start by understanding what RDT is. Real Device Testing involves testing mobile apps and websites on actual physical devices rather than relying solely on emulators or simulators. While emulators and simulators have their place in the testing toolkit, RDT brings a unique real-world perspective to the testing process. Unlike emulators and simulators, real devices have physical characteristics and quirks that can affect how an application functions. Real Device Testing bridges the gap between the digital realm and the physical world, allowing testers to identify issues that might not be apparent in simulated environments.The Need for RDT:-
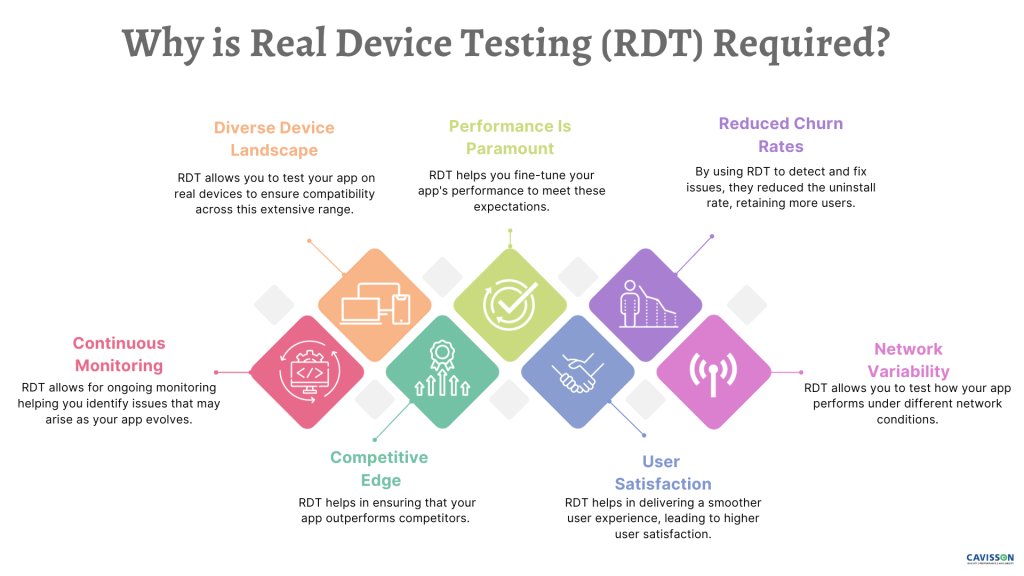
Why is Real Device Testing necessary? The answer lies in the multifaceted challenges posed by the vast mobile device landscape. Mobile app and web developers need to account for various screen sizes, operating systems, and hardware configurations, making it nearly impossible to test thoroughly on every possible device. Moreover, real devices offer insights into real-world user experiences. They account for factors like network conditions, device-specific issues, and hardware limitations, ensuring the application behaves as intended under diverse circumstances.Key Capabilities of RDT :-
1. Meaningful Performance Results:
RDT offers meaningful performance results by simulating real-world usage scenarios on actual devices. It provides insights into how an application performs in terms of responsiveness, speed, and resource utilization.
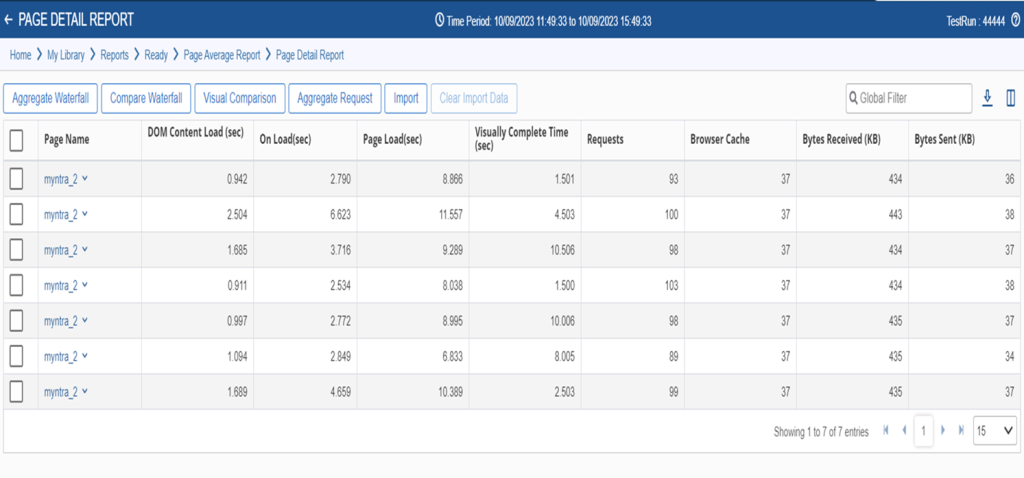
2.Timing Aggregation/Comparison:
RDT allows you to aggregate and compare timing data for different test scenarios. This helps understand the application’s performance across multiple devices and configurations, enabling you to fine-tune it for optimal user experience.
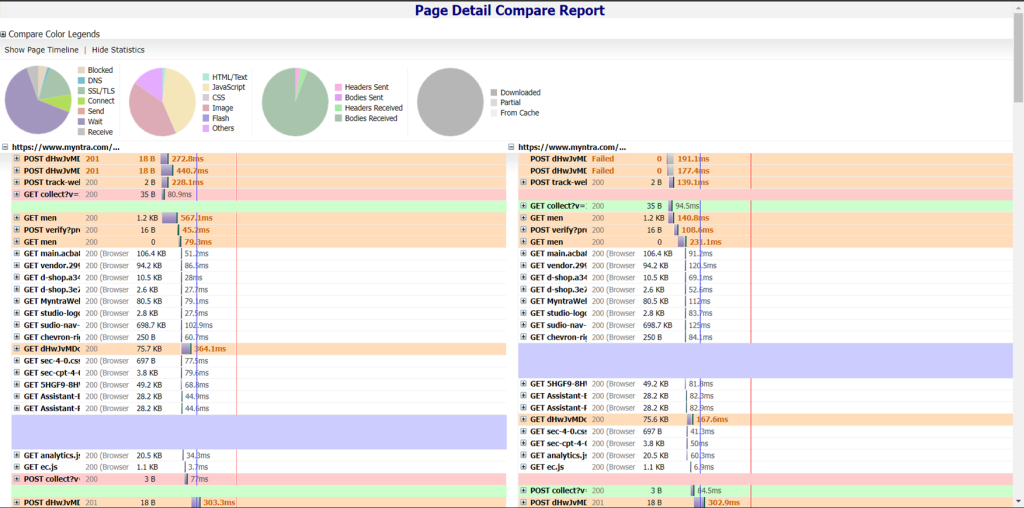
3. Rendering visual comparison:
RDT can compare the visual rendering of an application on various devices and browsers. This feature helps identify any rendering inconsistencies, layout issues, or design problems that could affect the visual appeal of your app.
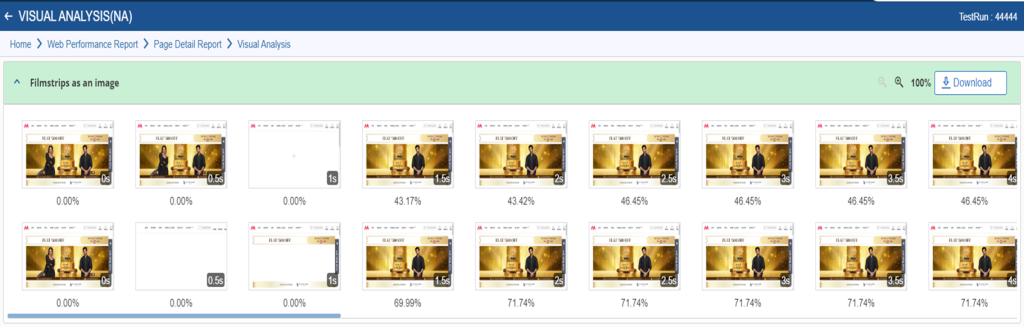
4. Recommendations:
RDT often provides recommendations and insights based on the test results. It suggests improvements and best practices to enhance the application’s performance, usability, and compatibility.
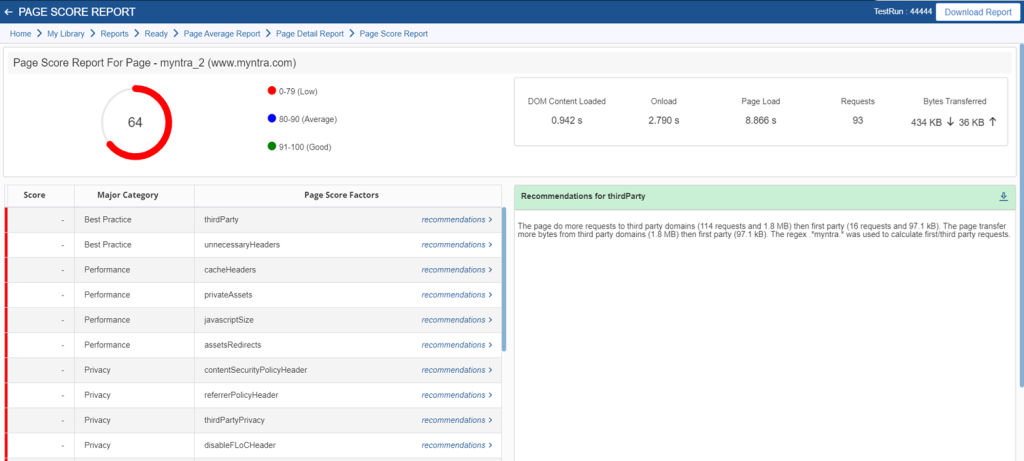
5. Integrated with Cavisson solution suite for server-side deeper diagnosis:
RDT can be integrated with Cavisson’s solution suite for deeper server-side diagnosis. This integration allows you to correlate performance data from real devices with server-side metrics, helping you pinpoint and resolve performance issues more effectively.
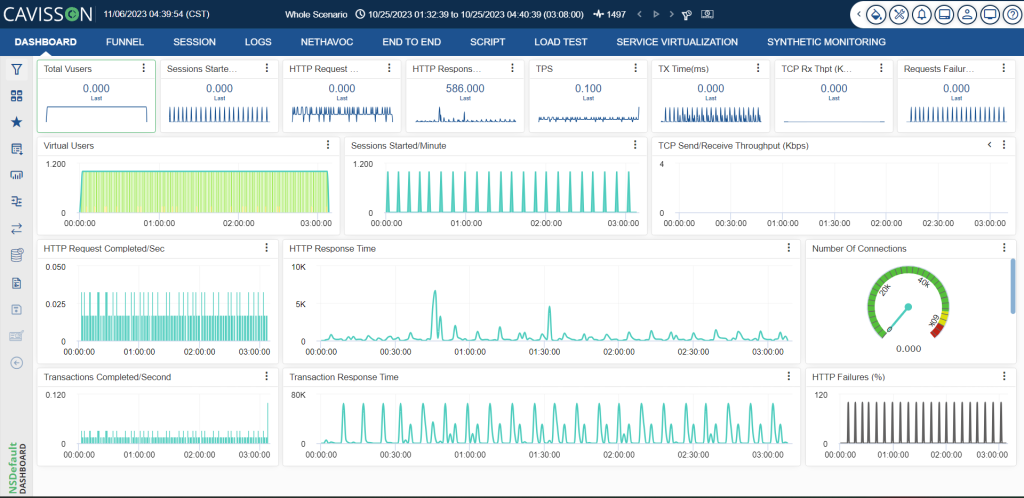
6. Ensure Exceptional Customer Experience of Applications on Customer Handsets/devices:
In our Performance Testing Platform, RDT ensures that your applications provide an exceptional user experience by testing them on real customer devices, such as smartphones and tablets. This approach helps identify and address device-specific issues that could impact user satisfaction.
7. Real Desktop browsers:
RDT isn’t limited to mobile devices; it also covers testing on real desktop browsers. This ensures that your web applications and websites perform well across different desktop environments, including various Device Types, Operating systems, browsers, and versions.
Future Trends in RDT:-
In the future, Real Device Testing (RDT) will continue to evolve to meet the demands of an ever-changing digital landscape. With the advent of 5G and beyond, RDT will be crucial in ensuring applications can harness the full potential of high-speed, low-latency networks. Additionally, the rise of edge computing will necessitate testing on edge devices to guarantee optimal performance in decentralized environments. Artificial intelligence will play a more prominent role in RDT, automating testing processes and providing deeper insights. IoT device testing will expand RDT’s scope to cover the growing array of connected devices.
Testing for extended reality (XR) applications will be essential, focusing on creating seamless immersive experiences. Test automation will continue to grow, improving testing efficiency. Security, sustainability, and energy efficiency will become key focal points, while global device coverage will ensure applications are accessible worldwide. Integration with DevOps and CI/CD pipelines will streamline testing processes, and RDT will place a higher emphasis on cross-platform compatibility and accessibility standards, ensuring that applications are both inclusive and reliable in an increasingly diverse digital landscape.
Conclusion:-
In conclusion, Real Device Testing (RDT) is more than a testing methodology; it’s necessary in a world where mobile apps and websites have become the lifeblood of businesses. It ensures that your applications are not only functional but also provide a seamless user experience on a vast array of real devices. Embracing RDT as a critical component of your testing strategy is the key to staying competitive in the digital landscape, meeting user expectations, and achieving success in a dynamic and ever-changing market.
Contact us today to kickstart your mobile application testing journey.

